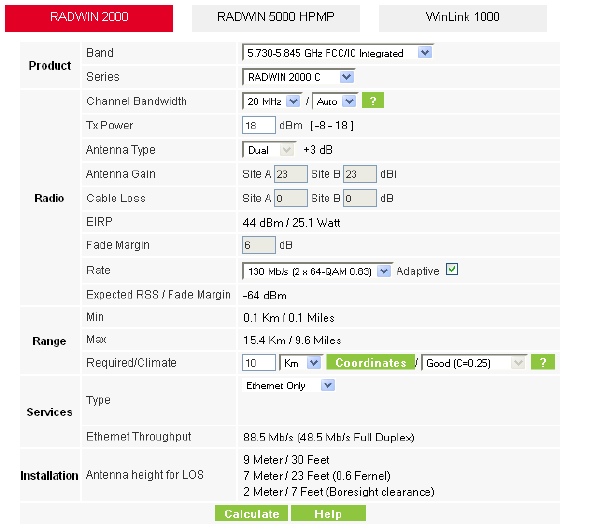
Using the RADWIN OLBC for RADWIN 2000
Continuing with the RADWIN OLBC for RADWIN 2000 Products:
Figure 2-1: Link Budget window
To use the Link Budget Calculator for RADWIN 2000:
1. Choose a band from the drop-down list.
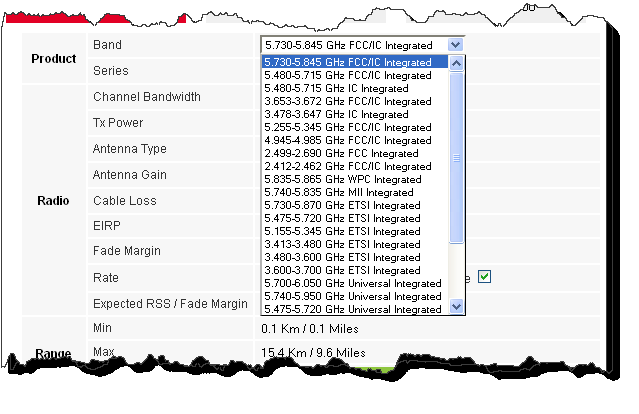
Figure 2-2: Band selector
2. Choose the Product Series. There are five products from which to choose:

Figure 2-3: Product Series selection
3. Choose the required channel bandwidth:
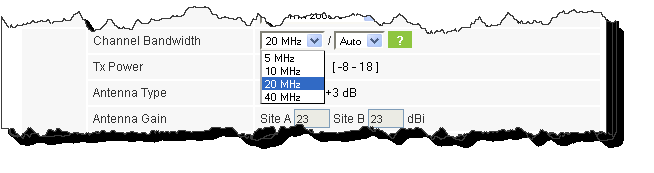
Figure 2-4: Channel bandwidth selection
4. For a collocated link choose the RFP. Use the Help button to the right of the RFP selection box for help:
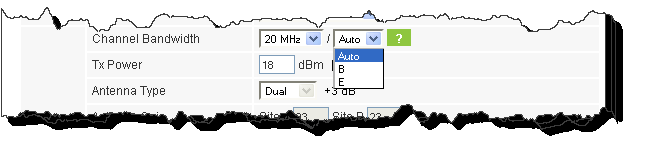
Figure 2-5: RFP Selector
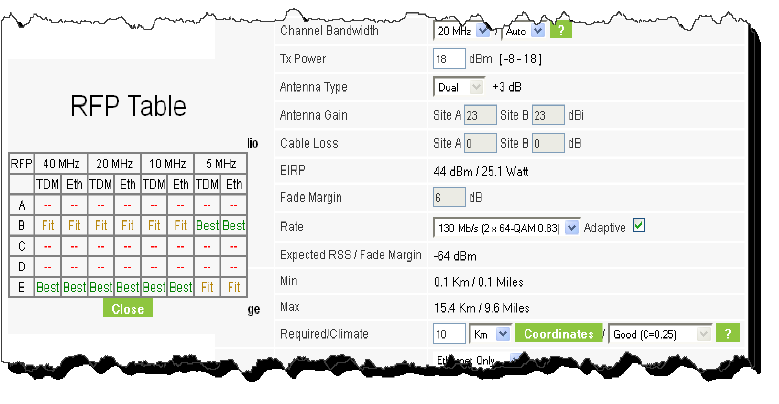
Figure 2-6: RFP Selection Guide
For collocated RADWIN 2000 products, you may only use RFP B or E.
5. Enter the required Tx power:
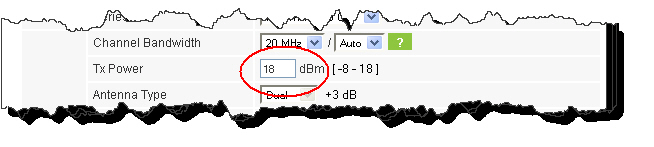
Figure 2-7: Selecting Tx Power
6. Enter the radio details. Note that Rate is chosen from a drop-down list:
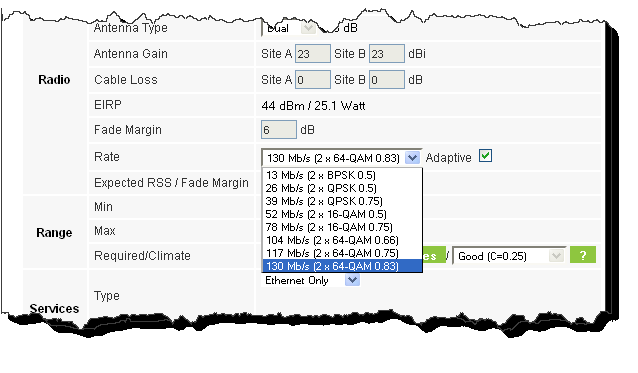
Figure 2-8: Rate selector
|
The Rate shown, defines the air-interface rate in Mbps. The system operates in TDD mode and has the overhead of the air-interface protocol. Thus, the Ethernet actual throughput is provided by the Ethernet Rate.
|
The Fade margin is the minimum required for LOS conditions. For degraded link conditions, a larger Fade margin should be used.
The EIRP is given in dBm and Watts.
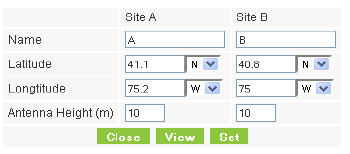
7. If the required range between the two link sites is known, you may enter it directly. Alternatively, you may enter the latitude and longitude of each site in the link, in which case the distance between them will be calculated and displayed.
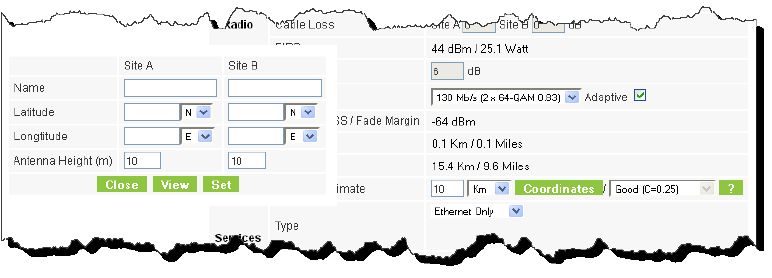
Figure 2-9: Calculation of distance from site coordinates
If for example, you enter:
Site A: 41.1°N lat 75.2°W Long
Site B: 40.8°N lat 75.0°W Long
and press Set,
the range will be calculated and displayed:
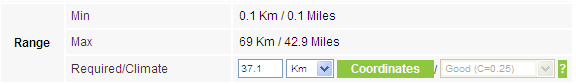
|
Alternatively, if you click View, you are offered a visual link profile in a new browser tab. See Chapter 5 for details.
8. Located to the right of the green Coordinates button is a drop-down list of Climactic C Factor values. It is only available if you choose a non-adaptive rate.
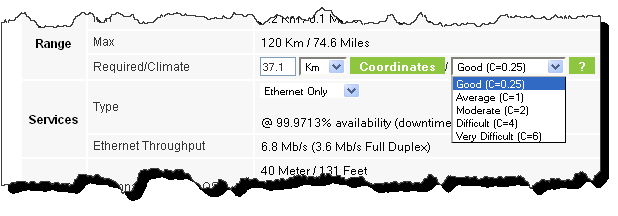
Figure 2-10: Climactic C Factors
For help about what these mean, click the  button to the right of the list in Figure 2-10.
button to the right of the list in Figure 2-10.
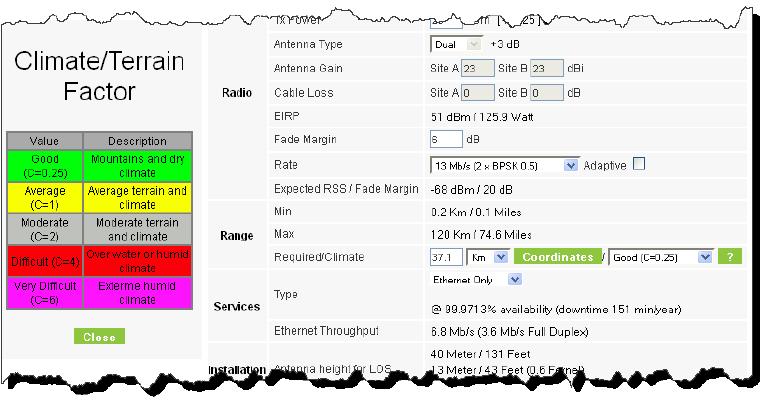
Figure 2-11: Climactic C Factor description
In Figure 2-12 we display a map of the world showing C Factor contours:
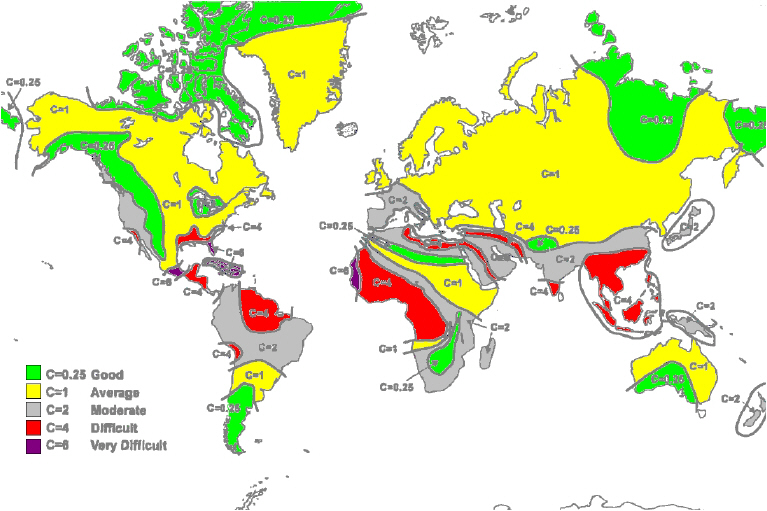
Figure 2-12: World map showing C Factor contours
9. After changing the C Factor, click Calculate to see the changed performance estimate.
10. Choose the required services:
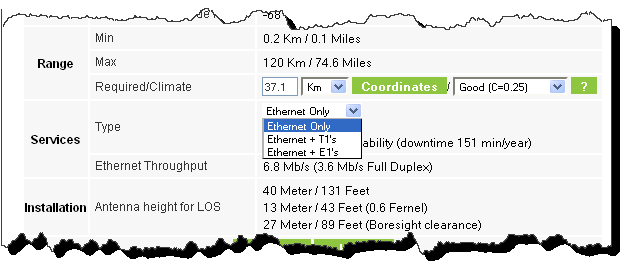
Figure 2-13: Services selector
Choosing Ethernet+T1s or Ethernet+E1s offers a further choice:
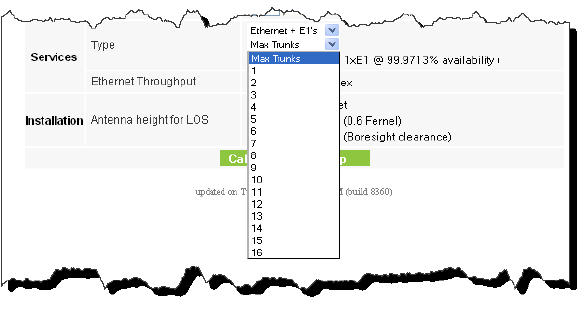
Figure 2-14: Choosing the number of trunks
11. Click Calculate to obtain the required performance estimate.
|
The Expected Performance parameters are calculated and displayed:
• Expected RSS - the expected RSS that the RADWIN Manager shows when the RADWIN 2000, RADWIN 5000 & WinLink 1000 ODUs are optimally aligned
• Services Type - max number of T1 or E1 trunks if “Max Trunks” is selected
• Ethernet Rate - maximum throughput available for the chosen parameter combination
• Antenna height for LOS – the minimum antenna height required for line-of-sight operation. It is the sum of the height required for boresight clearance due to the earth’s curvature plus the height required to clear the Fresnel zone
If the expected performance is not suitable for your application, try different parameters and repeat the calculation.